Introduction
Hypertension is a medical problem that can occur during a woman’s pregnancy. A pregnant woman is hypertensive if her blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg or more before 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Hypertension during pregnancy is divided into some categories:
- Pre existing hypertension (before pregnancy)
- Gestational Hypertension (Hypertension after becoming pregnant)
- Pre- Eclampsia ( Very high blood pressure with protein in the urine)
- Eclampsia (Fits)
Pre existing hypertension occurs in about 1 to 5% of pregnant women, while gestational hypertension occurs in 5 to 10% of pregnant women. If this disease is not controlled well during pregnancy, pre-eclampsia or eclampsia (fits) would occur. These complications can cause problems and death to the pregnant and her unborn fetus.
In Malaysia, uncontrolled hypertension during pregnancy is one of the major causes of maternal deaths. 20 to 33% of all maternal deaths are due to complications of hypertension in pregnancy.
 Photo 1: A Pregnant Lady Having Her Blood Pressure Checked
Photo 1: A Pregnant Lady Having Her Blood Pressure Checked
Who Is At Risk?
Hypertension during a pregnancy cannot be predicted. However, some women have the risk factors for this problem. The following factors can cause hypertension during pregnancy:
- Pre-existing hypertension
- Previous history of hypertension during pregnancy
- First pregnancy ( 2 times the risk)
- Obese women
- Age less than 20 years
- Age more than 40 years
- Multiple pregnancy (Twins, triplets)
- Molar pregnancy
- Suffers from chronic diseases like diabetes, kidney disease
- Suffers from anti phospholipid disease
- Suffers from connective tissue disease
Pre-Pregnancy Consultation
Always see your doctor for consultation with your spouse before getting pregnant. This consultation is called a pre-pregnancy consultation
During this consultation, your doctor will ascertain your medical problems which need to be treated or controlled before you get pregnant. If you already have pre existing hypertension, your anti hypertensive medication will be changed. Your doctor will prescribe antihypertensive medications that are safe for your future pregnancy. You will also be advised to take your medications as advised. This is to ensure that your hypertension is controlled before you become pregnant.
 Photo 2: Couple meeting a doctor before pregnancy
Photo 2: Couple meeting a doctor before pregnancy
What Are The Medications That You Can Take During Pregnancy?
There are some antihypertensive medications that can cause adverse effects in a fetus. Hence, you should take medications that do not affect your baby.
Example of medications that can be taken during pregnancy:
- Nifidipine
- Methyldopa
- Labetolol
Example of medications that should not be taken during pregnancy:
- Perindopril
- Enalapril
- Captopril
- Telmisartan
- Irbesartan
- Losartan
Management Of Hypertension During Pregnancy
During your pregnancy, the doctor or nurse will set up a follow up appointments to manage your pregnancy better. You will be monitored to ensure that your blood pressure is well controlled. You will also be asked about symptoms of uncontrolled blood pressure. Symptoms of uncontrolled blood pressure are:
- Pounding headache
- Giddiness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Blurred eyesight
- Upper abdominal pain
- Swollen feet
The medications that you are taking will also be monitored, either to increase or decrease the dosage to stabilize your blood pressure. This management will be continued until you deliver your baby. If you have any complications, you might be admitted to a hospital for better care. If you suffer from pre-eclampsia or eclampsia, your baby must be delivered to save your life. Generally, hypertension that occurs during your pregnancy will resolve after the birth of your baby. Pre-existing hypertension will persist after deliver.
 Photo 3: Nurse Screening A Pregnant Lady
Photo 3: Nurse Screening A Pregnant Lady
 Photo 4: Nurse Checking The Pregnant Lady’s Blood Pressure
Photo 4: Nurse Checking The Pregnant Lady’s Blood Pressure
What Are The Complications That Can Occur?
A number of complications can occur to the mother and the fetus throughout the pregnancy and after the delivery.
- Complications to the pregnant lady
- Pre-eclampsia
- Swollen body
- Kidney damage
- Liver damage
- Dangerous bleeding
- Eclampsia – brain damage that causes fit
- Death
 Photo 5: Very High Blood Pressure
Photo 5: Very High Blood Pressure
 Photo 6: Swollen Feet
Photo 6: Swollen Feet
 Photo 7: Lady With Eclampsia
Photo 7: Lady With Eclampsia
- Complications to the fetus
- Reduced weight gain
- Sudden death
- Preterm birth
- Death due to complications of preterm birth
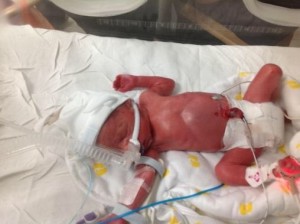 Photo 8: Preterm Baby
Photo 8: Preterm Baby
Management After Delivery
The risk of complications from hypertension during pregnancy remains until about 6 weeks after delivery. During this period, the nurse will monitor the blood pressure control of the new mother during home visits. If the blood pressure is uncontrolled, the nurse will refer her to see a doctor. The mother will also be given advice regarding the need to either stop or continue taking the medications. If she needs to continue the medication, the mother will see the doctor in the clinic regularly for monitoring until the six weeks are completed. Mothers who have pre existing hypertension can revert back to their former medications.
 Photo 9: Home Visit
Photo 9: Home Visit
Treatment During Breastfeeding
The new mother is encouraged to exclusively breastfeed her baby for at least six months. A breastfeeding mother can take most antihypertensive medications. Although these medications are released in the breast milk, the quantity is too small to affect the baby. Remember, stopping the medications will harm the mother. Always discuss with your doctor regarding your medications during breastfeeding.
Examples of medications that should not be taken by a breastfeeding mother:
- Metoprolol
- Atenolol
- Furosemide
- Hydrochlorothiazide

Photo 10
References
- Carson MP, Chih TCP, Gobson PS et al (March 2014). Hypertension and Pregnancy. Retrieved August 27 2014 from emedicine.medscape.com
- Hypertension in Pregnancy: The Management of Hypertensive Disorders During Pregnancy. NICE Clinical Guidelines. No 107. Aug 2010.
- Malaysian CPG Management of Hypertension 4th Edition.
| Last Reviewed | : | 2 March 2016 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Sheela Bai a/p Pannir Selvam |
| Translator | : | Dr. Sheela Bai a/p Pannir Selvam |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Ainol Shareha Binti Sahar |
 PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia
PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia