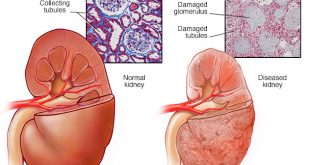
It is very important to slow down the progression of diabetic kidney disease (DN) and protect against other diabetes complications. This will reduce long-term ill-health and premature deaths .
What can you do?
Make healthy diet/ lifestyle changes
Protein restriction
- A low protein diet of 0.6 – 0.8 g/kg/day may be helpful in slowing progression of kidney disease
- Dietary protein restriction should be supervised by a dietician
- Important to ensure adequate energy intake i (30 – 35 kcal/kg/day) to prevent protein-energy malnutrition
Sodium restriction
- Increasing sodium intake is associated with worsening protein leak in urine and increased blood pressure levels
- Hence, it is advisable to restrict total intake of sodium to < 2,400 mg/day
- A low sodium diet also enhances the effects of certain medications known as ARBs/ ACEIs that are usually recommended for people with diabetic kidney disease
Smoking cessation
- Cessation of smoking slows the decline of renal function and will also reduce the risk of disease of the heart and blood vessels. (Cardiovascular disease or CVD)
Achieve optimum weight
- For patients who are obese, weight reduction has been shown in some studies to retard the decline in renal function and reduce ‘proteinuria’
- Weight reduction can be achieved with the following measures :
- increased exercise ( recommended 20 minutes /day but please refer to “rehabilitation of patients with end-stage renal disease” article on how to exercise safely)
- Reduced intake of saturated fat, cholesterol and calories
Patients with chronic kidney disease are at increased risk of cardiovascular disease ( see section Cardiovascular disease in CKD. Hence, apart from measures slowing down kidney disease progression, the following issues should be addressed:
Correction of abnormal lipid levels
- A blood test known as a “Full lipid profile” should be performed at least once a year to check on the level of fats in your blood
- If this test is abnormal , you should be advised on how to make lifestyle changes in your diet, exercise, etc . Blood tests should be repeated to check that target levels are achieved.
- The target to achieve:+ LDL cholesterol less than 2.6 mmol/l . However, the target may be set even lower for those with known coronary artery.
- The usual drug therapy given to lower LDL-cholesterol levels is Statin therapy . Statin is recommended in patients with diabetes when LDL-cholesterol levels exceed 2.6 mmol/L. Is has been shown to prevent cardiovascular events in patients with CKD and raised lipid levels.
Antiplatelet agent
- Aspirin should be used in patients with DN who are known to have cardiovascular disease or who are considered at high risk of developing cardiovascular disease – this risk needs to be assessed by your doctor.
References
Malaysian Clinical Practice Guideline: Diabetic Nephropathy July 2004
Malaysian Clinical Practice Guideline: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Adult 2011
Malaysian Clinical Practice Guidelines : Management of Dyslipidaemia 4th edition, 2011
| Last Reviewed | : | 3 May 2016 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Shahnaz Shah Firdaus Khan |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Sunita Bavanandan |
 PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia
PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia