Diabetes mellitus can cause long-term problems in the eye, kidney and nerves because of damages to small blood vessels in these tissues. Diabetes mellitus also causes damages to large blood vessels supplying the heart, brain and legs leading to heart attacks, stroke and limb loss respectively. People with poor diabetes control are more likely to get these problems. The higher the average blood sugar levels, the greater is the risk of developing these problems.
As children with diabetes have the disease in earlier part of life, they have a longer duration of disease compared to individuals with adult onset diabetes. This puts them at higher risk of developing long-term diabetes complications. Therefore good diabetes control in childhood and adolescent years is very important to try to prevent the long-term complications. They need to be checked or screened for these long-term problems during the teenage years if they already have diabetes as a child. The purpose for the screening examination or test is to detect the early stage of the problem before it manifests as symptoms and to treat early to prevent it from getting worse.
- Eye Problem (Diabetes Retinopathy)
What is the eye problem ?
Retina is the thin layer of tissue at the back of the eye that is vital for normal vision. Retinopathy refers to damage to the retina and can cause blindness (see Figure 1). Diabetes retinopathy is generally divided into non-proliferative retinopathy and proliferative retinopathy.
Non-proliferative retinopathy refers to the early abnormal changes to the retina which do not impair vision and require no eye treatment. They may resolve with improvement of diabetes control.
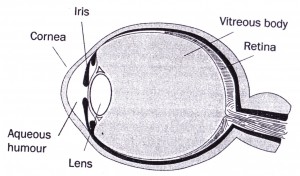 Figure 1 : The eye seen in cross-section
Figure 1 : The eye seen in cross-section
Proliferative retinopathy refers to the more severe abnormalities in the retina with new blood vessel formation. It causes loss of vision and needs eye laser treatment by the eye doctor (ophthalmologist). Poor diabetes control and teenage years can cause eye damage to progress from non-proliferative to proliferative stage.
Why do the eye problem screening ?
Early damage to the eye caused by diabetes can occur in teenagers with diabetes since childhood. The early eye problem usually does not cause symptoms. The patient does not know he/she has the eye damage unless the eyes are examined by a doctor. Therefore screening examination is necessary to detect these abnormalities, monitor its progression and treat if needed to prevent blindness.
When to do the eye problem screening ?
For children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus, eye damage is often not found in those less than 10 years of age. Therefore the recommendation is to start screening for eye complications from 11 years of age with 2 years of diabetes and from 9 years of age with 5 years of diabetes duration. The eye examination should be repeated every year.
For children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes mellitus where eye damage is more commonly found, the recommendation is to start screening for eye complications at the time when the diabetes is diagnosed. The eye examination should be repeated every year.
How is the eye problem screening done ?
The eye examination is usually done by an eye doctor (ophthalmologist) with a medical equipment. It does not cause any pain or discomfort to the patient.
- Kidney Problem (Diabetes Nephropathy)
What is the kidney problem ?
Kidneys are the major organ in the body to process waste products and get rid of them by passing them out of the body as urine. Diabetes nephropathy refers to the kidney damage caused by poor diabetes control. It can progress to kidney failure which needs dialysis treatment (blood from the body goes through a machine which acts like kidneys to filter out waste products) and can cause early death.
In the early stage of kidney damage due to diabetes, the kidneys leak out small amount of protein in the urine (called microalbuminuria) which can be detected by a urine test. Children and adolescents with poor diabetes control can develop microalbuminuria.
Why do the kidney problem screening ?
The early kidney damage does not cause symptoms. The patient does not know he/she has the problem unless a urine test is done to show the abnormality.
If the urine test is persistently abnormal, a medication in the form of tablet can be started to slow the progression of the kidney damage in addition to improving diabetes control. The medicine used is also used to treat high blood pressure or hypertension which can be present in kidney disease.
When to do the kidney problem screening ?
For children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus, kidney damage is often not found in those less than 10 years of age. Therefore the recommendation is to start screening for kidney complications from 11 years of age with 2 years of diabetes and from 9 years of age with 5 years of diabetes duration. The urine test should be repeated every year.
For children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes mellitus where kidney damage is more commonly found, the recommendation is to start screening for kidney complications at the time when the diabetes is diagnosed. The urine test should be repeated every year.
How is the kidney problem screening done ?
A urine test is done on the first morning urine passed. If it is abnormal, the test is repeated with two further urine samples. Kidney damage is confirmed if 2 out of 3 urine samples show abnormal results.
- Nerve Problem (Diabetes Neuropathy)
Poor diabetes control can cause damage to the nerves (neuropathy) controlling muscle movement, sensation and internal organ system function like gut, bladder and blood pressure control. In the early stage, the neuropathy can improve with good diabetes control.
Diabetes neuropathy is uncommon in children & adolescents with diabetes compared with the adults.
It can cause numbness, ‘pins & needles’ sensation and persistent pain. It can be detected by physical examination especially sensation testing by a doctor.
The screening examination is recommended from age 11 years with 2 years of diabetes duration.
- Large blood vessel damage and problems
Atherosclerosis is the gradual process of large blood vessel wall damage that leads to heart attacks (cardiovascular disease) and stroke.
Poor diabetes control in children and adolescents worsens and accelerates atherosclerosis. Hence they are more likely to have heart attacks and associated deaths in adulthood.
Having high blood pressure (hypertension), blood lipid/cholesterol abnormalities and smoking further increase the risk of heart attacks later in life in children and adolescents with diabetes.
High blood pressure and blood lipid/cholesterol abnormalities do not cause symptoms usually. The patient does not know he/she has the problem unless the blood pressure is measured and a blood test is done to detect cholesterol abnormalities.
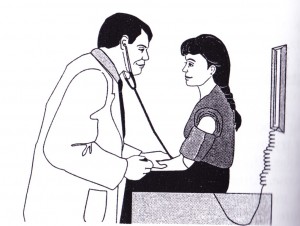 Figure 2 : Measurement of blood pressure
Figure 2 : Measurement of blood pressure
It is recommended that children and adolescents with diabetes have their blood pressure checked at least once a year to screen for hypertension. Medication to treat hypertension can be started if necessary.
To screen for lipid/ cholesterol abnormalities, blood test for lipid/cholesterol levels after an overnight fast of at least 8 hours should be done in children with diabetes above 12 years of age when the diabetes is stabilized. If there is family history of high blood cholesterol or early death due to heart attacks, screening blood test should start at age 2 years according to international recommendation. The lipid test should be repeated every 5 years if results are normal.
It is important to maintain a healthy body weight in children and adolescents with diabetes as obesity is associated with high blood pressure and abnormal cholesterol levels. The family plays a vital role in helping a child with diabetes to maintain a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise to prevent obesity and aid diabetes control to prevent complications.
Every effort should be made to prevent an adolescent with diabetes to stop smoking to reduce the progression of diabetes complications.
Reference
- Donaghue K, Chiarelli F, Trotta D, Allgrove J, Dahl-Jørgensen K. (2011). Microvascular and macrovascular complications. In Global IDF/ISPAD Guideline for Diabetes in childhood and adolescence (Chapter 17, pp.115). Retrieved February 4,2013, from http://www.idf.org/global-idfispad-guideline-diabetes-childhood-and-adolescence
- Type 1 diabetes in children, adolescents and young adults. Dr Ragnar Hanas 2nd edition. Complications in blood vessels. Figure 1, pg 307. Figure 2, page 310.
 PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia
PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia