What Is Asthma?
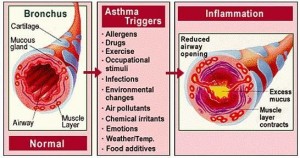
Asthma is a chronic lung disease that causes episodes of difficulty in breathing. Asthma symptoms are caused primarily by chronic inflammation of the airways. This makes the airways of the patient with asthma highly sensitive to various triggers. Examples of triggers such as dust, animal furs, extreme weather change and exercise.
When the airways is triggered by any type of external or internal factors, the airways swell and fill with mucus. Muscles within the airways will contract which can lead to further narrowing of the airways. The airways narrowing makes it difficult for the air to be breathed out from the lungs and it lead to various symptoms of asthma. The asthma can affect people of all ages including breast feeding mother.
Why is it important to use inhaled steroid in asthma patient?
As asthma is a chronic inflammatory condition of the airways, anti-inflammatory drugs such as steroid inhaler is one of the main treatment for asthma patients. Reducing the inflammation of the airways will further decrease the bronchial hyper-responsiveness and asthmatic attack.
The types of anti-inflammatory medications include:
- Inhaled steroid
Inhaled steroid is the main preventive drugs in asthma. It should be taken via inhalation route and the dosage should be kept to a minimum to reduce side effects (side effects usually occur locally).
Even though asthma cannot be cured, but appropriate used of inhaled steroid can improve asthmatic control. Therefore, patient may have fewer and less severe asthmatic attacks. Without appropriate treatment, patient will have more frequent and severe asthmatic attacks
- Oral steroids
Short term oral steroid may be used for treatment of acute attack of asthma (Acute Exacerbation of Bronchial Asthma). However, long-term oral steroids is rarely used for severe uncontrolled asthma.
What are the impacts/ complication of uncontrolled asthma?
If inhaled steroid is not used appropriately, patient will have uncontrolled asthma and frequent asthmatic attack. It can become a major problem that will interfere with patient’s daily activities, for examples:
- More severe asthma can interfere with daily activities such as work, sleep or recreational activities
- Patients will have to take frequent sick leave and absence from work during asthma attacks
- Frequent emergency room visits and hospitalizations for severe asthma attacks
- Side effects from prolonged use of certain medications used to treat severe asthma eg. oral steroid
- May lead to a life-threatening asthma attack
With proper treatment, asthma patient can have very few symptoms, if any, and they can lead a normal, active live and sleep through the night without interruption from asthma.
Is it safe to use steroid inhaler in breast feeding mother?
Asthma control in the breast feeding mother is as important as for other non-pregnant women, and the risk of asthma exacerbation is similar in both groups.
There are limited studies about the safety of asthma drugs during breastfeeding. Published studies in the postpartum period have been small case series with generally short follow-up.
However, evidences have shown that inhaledsteroid are safe to be used in nursing mothers, i.e.:
- Systemic absorption of inhaled steroid is generally minimal and causes little harm to the infant
- The infant’s exposure during breast feeding is 10 to 1000 times less than during in the mother’s womb.
- The amount ingested through the mother’s breast milk is far below the therapeutic level for an infant e. mostly under 3% of a therapeutic dose per kilogram body weight
Therefore, it is recommended that breast feeding women should be encouraged to continue with the inhaled steroid if they have used it before pregnancy, especially if this regimen adequately controlled their asthma.
In summary
Asthma is a chronic lung disease that can cause episodic symptoms which might interfere with daily activities or even can lead to life-threatening attack. The used of inhaled steroid is important to improve asthma control and prevention of both short-term and long-term complications caused by asthma.
Breastfeeding should be continued in women with asthma even though they are on inhaled steroid. In general, asthma medications including inhaled steroid are safe during lactation and the benefits outweigh any potential risks to the baby.
References
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Expert Panel Report 3 (EPR3): Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma. Accessed: April 30, 2014.
- Ministry Of Health Malaysia. Clinical Practice Guidelines For Management Of Adult Asthma 2002.
- Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention: Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) (Updated 2012)
- British Thoracic Society. British Guideline on the Management of Asthma-a national guideline 2008.
- Lim A, Hussalny SY, Abramson MJ. Asthma drugs in pregnancy and lactation. Australian Prescriber 2013;36(5):150-153.
- Lokeln YC, editor. Pregnancy and breastfeeding medicines guide. Melbourne: Pharmacy Department, Royal Women’s Hospital; 2010.
- Ilett K, Kristensen J. Drug use and breastfeeding. Expert Opin Drug Saf 2005;4:745-68.
- Lawrence R, Schaefer C. General commentary on drug therapy and drug risk during lactation. In: Schaefer C, Peters P, Miller RK, editors. Drugs During Pregnancy and Lactation: Treatment Options and Risk Assessment. 2nd ed. London: Elsevier; 2007. p. 609-20.
- Fält A, Bengtsson T, Kennedy B-M, Gyllenberg A, Lindberg B, Thorsson L, et al. Exposure of infants to budesonide through breast milk of asthmatic mothers. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007;120:798-802.
| Last Reviewed | : | 15 July 2015 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Ho Bee Kiau |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Azza bt. Omar |
 PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia
PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia