Exercise induced asthma happened when the airways narrowed (get smaller) as a result of strenuous exercise. Nowadays, exercise induced bronchoconstriction is the preferred term for this condition. Exercise does not cause asthma, but it can trigger asthmatic attack. Majority of people who experienced exercise induced bronchoconstriction have underlying chronic asthma. But normal individuals who do not have bronchial asthma or allergic rhinitis may experience this condition as well. It is usually under diagnosed as the symptoms were not reported or a person with exercise induced bronchoconstriction will self-limit his or her physical activities.
Symptoms
The symptoms of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction occur typically 5-10 minutes after stopping from a strenuous exercise. They are less common during exercise but may begin after 5 to 20 minutes of non-stop exercise. This occurs because the airway is exposed to sudden changes in temperature and humidity of the inhaled air as a result of faster breathing during exercise. Most common symptoms include:
- Coughing
- Chest tightness or chest pain
- Wheezing (hoarse, squeaky, whistling or musical sound)
- Shortness of breath when exercising
- Unusual fatigue while exercising with prolonged recovery after stopping
Symptoms usually disappear on their own after 30- 45 minutes after discontinuation of an exercise. The onset and offset of symptoms suggestive of exercise induced bronchoconstriction are very important to differentiate with physical unfitness. Symptoms are more severe in people who have exercise-induced bronchoconstriction.
Diagnosis
Symptoms alone is not a good way to diagnose exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. Vocal cord dysfunction, irregular heartbeats induced by exercise, chronic lung diseases and reflux esophagitis can present with similar symptoms .Common way to test the lung function is by doing a spirometry. It will measures the amount of air you breath out and how fast you can blow it out. It will be done before and after a supervised intense exercise, either using a treadmill or ergometer in order to provide evidence of bronchoconstriction with exercise. The exercise will take 6 to 10 minutes, to achieve desired heart rate.
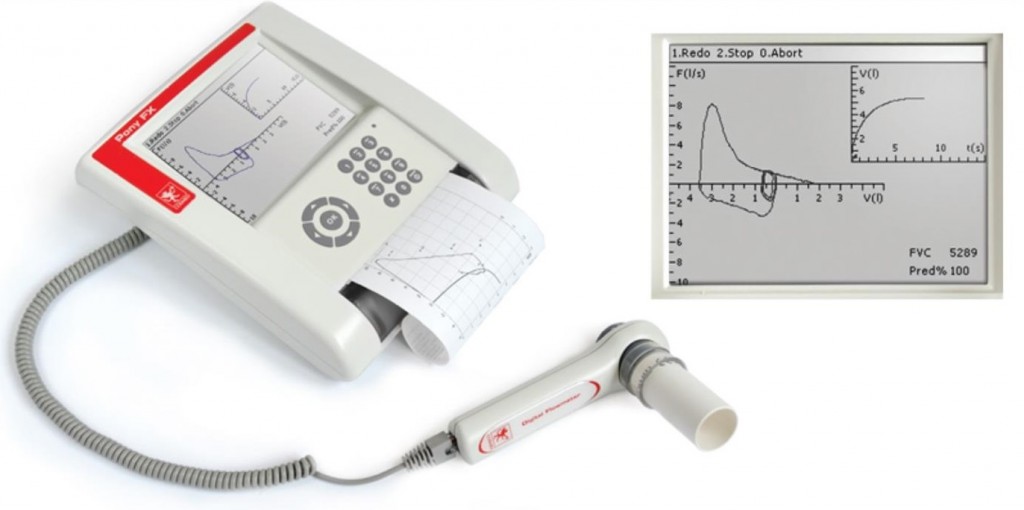
Spirometer
Source: www.balasoriyahospital.Ik
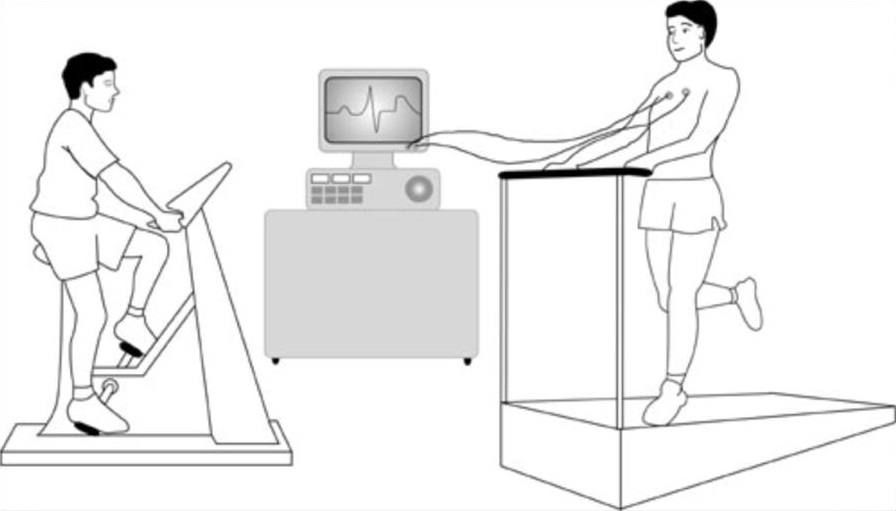
Treadmill and ergometer exercise testing
Source: www.sads.org.uk
Apart from the exercise challenge test, there are alternative tests that can be done to proof airway hyper responsiveness. Methacholine or mannitol challenge test are the examples of bronchial provocation tests.
Complications
Untreated exercise induced bronchoconstriction can lead to physical inactivity. Physical inactivity causes multiple medical problems such as hypertension and obesity. Although it is not common to get severe respiratory distress during exercise, but if it is left untreated it can be fatal.
What are the benefits of exercising?
- Makes your heart and lung stronger
- Increases energy level
- Helps to sleep better and improves concentration.
- Reduces stress and anxiety.
- Improves your immune system and helps to combat nasty infections causing cold or flu.
References
- http://www.thorasic.org>allergy-asthma
- www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov>punned
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/exercise-induced_bronchoconstriction
| Last Reviewed | : | 19 May 2016 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Azlina bt. Samsudin |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Jamalul Azizi Abdul Rahaman |
 PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia
PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia


