Diabetes, Monitoring, Monitoring of Complications (+8)
Introduction Proteinuria means the presence of protein in the urine. The most common kind of proteinuria is characterised by the presence of albumin in the urine. Normally the kidneys will prevent protein from being excreted into the urine. In circumstances where the blood protein is high, it may appear in …
Read More »
Diabetes, Monitoring, Monitoring of Complications (+8)
Introduction Renal profile is a test to assess kidney health. It is useful to measure kidney function. Renal profile gives information on levels of creatinine, sodium, calcium, chloride, blood urea and potassium. Some laboratory calculates glomerular filtration rate too. Kidney plays an important role in maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance. …
Read More »
Diabetes, Monitoring, Monitoring of Complications (+8)
Introduction Lipid profile or lipid panel is a measurement of different types of cholesterol and level of triglyceride in the blood. It is a collective term given to the estimation of total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-L), low-density lipoprotein (LDL-L) cholesterol and triglyceride. An extended lipid profile may include very …
Read More »
Diabetes, Monitoring, Monitoring of Complications (+8)
Introduction Monofilament examination is used to assess high risk foot for diabetes foot ulcers. It is to assess pressure sensation perception. It is reliable in screening for patients at risk of foot ulceration because sensitivity is a more important parameter [1]. Monofilament examination is inexpensive and non invasive. What Is …
Read More »
Diabetes, Monitoring, Monitoring of Complications (+8)
Introduction Foot examination is part of an integral management of diabetes. Foot problems may develop after more than 10 years of diabetes duration. Diabetes foot ulcers develop secondary to chronic ischaemia (insufficient blood supply to the foot) due to microvascular (small vessels) and macrovascular (large vessels) complications of diabetes (5]. …
Read More »
Diabetes, Monitoring, Monitoring of Complications (+8)
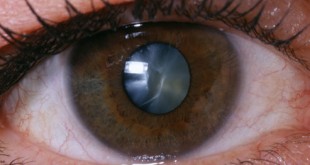
Introduction The eye is an important organ that allows vision. Retina is part of the eye that consists of a number of cells and normal vision depends on intact-cell communication among them. Diabetes and chronic exposure to hyperglycaemia (high glucose in the blood) damages all the major retinal cells of …
Read More »
Diabetes, Monitoring, Monitoring of Complications (+8)
Introduction Erectile dysfunction (ED) is defined as the persistent or recurrent inability of a male to attain and / or maintain a penile erection. This inability leads to insufficient sexual performance [1]. Diabetes is a risk factor for ED and affects approximately 34 to 45 percent men [2]. ED is …
Read More »
Diabetes, Monitoring, Monitoring of Complications (+8)
Introduction ECG is a test assessing the electrical activity of the heart. It is detected by electrodes attached to the outer surface of the skin and recorded by a device external to the body [1]. The electrodes are placed across the chest and it records electrical activity of the heart …
Read More »
 PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia
PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia