What is Diabetes Mellitus?
Diabetes Mellitus or commonly abbreviated as DM is a disease that is not foreign to us in the community. This disease is also known as ‘kencing manis’ in Bahasa Malaysia and suffered by the young and old.
People with diabetes have high blood sugar in the blood and is called hyperglycemia. Approximately 20.1% populations aged over 30 years in Malaysia (National Health and Morbidity Survey 2011) have diabetes.
Unfortunately many people are not aware that they are diabetic until it becomes chronic and symptoms of hyperglycaemia become apparent.
Perhaps many people are asking, what is diabetes mellitus, what can cause diabetes mellitus and why does diabetes occurs?
In general, diabetes mellitus is caused by a malfunction of the pancreas, an organ that produces insulin hormone resulting in lack of insulin production. Insulin is necessary in facilitating glucose to enter the cell. Glucose is needed in the cell for energy. Energy is vital in maintaining metabolism, organ function and health.
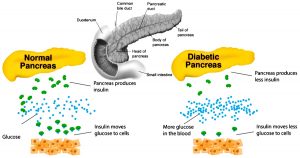 Figure 1 : Normal and diabetic pancreas ( source : http://abcblogs.abc.es/eat-fit )
Figure 1 : Normal and diabetic pancreas ( source : http://abcblogs.abc.es/eat-fit )
Overweight and obesity can impair insulin function, thus causing diabetes. In this situation, excess fat cells in obese individuals cause insulin becoming insensitive and hamper the influx of glucose into cells.
There are two main types of diabetes :
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
see : Diabetes mellitus
Type 1 DM patients will need insulin upon diagnosis and this type of diabetes occurs in the younger age population.
In type 2 DM, patients do not need insulin upon diagnosis but oral anti-diabetes agents are used to control high sugar level. Nevertheless these patients may need insulin in later duration of the disease. Type 2 DM occurs among older population but teenagers are becoming increasingly diagnosed with type 2 DM due to overweight, obesity and sedentary lifestyles.
Other causes of diabetes are pancreatic diseases for example pancreatic cancer, genetic predisposition, infection at the pancreas resulting in damage to the beta cells and medication use such as long-term steroid therapy.
For type 2 diabetes mellitus sufferers, blood sugar levels control can be achieved through changing lifestyle and eating habits.
According to various studies, the lifestyle changes have been proven effective in reducing the risk of diabetes and achieving optimum control of the disease. Therefore, it is very important for you to know if you have diabetes.
What are the signs and symptoms of diabetes?
Signs and symptoms of diabetes may not be experienced by everyone. Common signs and symptoms are :
1. Increase micturation frequency and amount of urine (polyuria)
2. Increase thirst causing to increase drinking (polydipsia)
3. Excessive hunger or eat a lot (polyphagia)
4. Frequent urination with glucose in the urine (glycosuria)
5. Sudden significant weight loss
6. Numbness over feet and hands (extremities)
7. Easily tired and feel weak all the time
8. Blurring of vision
9. Wounds heal slowly
10. Prone to infection especially over the skin.
For Type 1 diabetes, the main symptoms of this disease are abdominal pain, sudden weight loss and constant thirst.
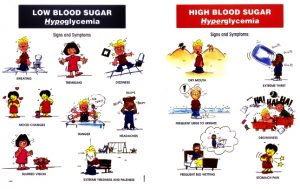 Figure 2 : Signs and symptoms of diabetes mellitus (source : www.fullissue.com)
Figure 2 : Signs and symptoms of diabetes mellitus (source : www.fullissue.com)
What can you do?
A person is said to be suffering from diabetes when his fasting blood sugar level is more than 7.0 mmol/L or more than 11.1 mmol/L in a non-fasting state. However, many of the symptoms of diabetes occur only when blood sugar is greater than 15 mmol/L.
Do not wait until you get the symptoms of diabetes. The only way to know is to have a blood test.
Screening test can be done at any health clinics in Malaysia and annual check-up is recommended.
Conclusion
Prevention is very important and you are advised to seek intensive treatment if you wish to avoid complication of diabetes.
If you have diabetes risk-factors, you are encouraged to undergo screening for blood sugar level at least once a year.
If diabetes is not taken care early, complications in the blood vessel can occur in the brain, eyes, heart, kidneys and legs. These complications can lead to heart attack, stroke, kidney failure, blindness and diabetes foot ulcer that could lead to amputation. In addition, diabetics are also very susceptible to infection in the lungs, teeth, and gums and in the urinary tract.
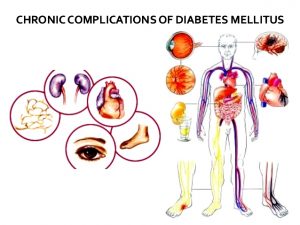 Figure 3 : Diabetes complications (source : static.wixstatic.com)
Figure 3 : Diabetes complications (source : static.wixstatic.com)
Prevention is better than cure. You can reduce the risk of diabetes complications by recognizing the signs and symptoms of diabetes early.
Here are some sources of information and support options available :
| Name of organization | ||
| 1 | National Diabetes Institute (NADI) No. 1, Jalan SS 3/50,University Garden,47300 Petaling Jaya,Selangor, Malaysia Telephone : 03-78761676 / 78761677 Fax : 03-78761679 E-mail : enquiry@nadidiabetes.com.my Website : www.nadidiabetes.com.my |
 |
| 2 | Persatuan Diabetes Malaysia (PDM) Secretariat: No. 2, Lorong 11/4E, 46200 Petaling Jaya Selangor Darul Ehsan Tel: 03-79574062/ Fax: 03-79604514 Website: http://www.diabetes.org.my Email: info@diabetes.org.my |
 |
| 3 | Nutrition Society of Malaysia (NSM). http://www.nutriweb.org.my |  |
| 4 | Malaysian Endocrine & Metabolic Society (MEMS)
Department of Medicine, 8th Floor, Clinical Block, UKM Medical Centre (PPUKM),
Office:
|
|
| 5 | Health clinics with Non-Communicable Disease Program organize support groups for their clients – check with your nearby health clinic or district health office for availability |
Reference
- Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Type 2 Diabetes mellitus (4th Edition) 2009. Ministry of Health Malaysia. MOH/P/PAK/184.09 (GU).
- Davidson’s Principle and Practice of Medicine (21st Edition) 2010. Nicki R, Brian R and Stuart H. Churchill Livingstone.
 PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia
PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia