Introduction
Hypertension is defined as persistent elevation of systolic blood pressure of 140mmHg or greater and/or diastolic blood pressure of 90mmHg or greater.
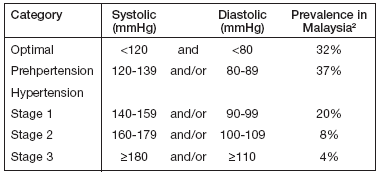
Table 1: Classification And Prevalence Of Hypertension For Adults.
The metabolic syndrome also known as syndrome X or insulin resistance syndrome is not a disease but a cluster of metabolic abnormalities that increased the likelihood of developing diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease. The abnormalities included obesity, hypertension, high blood sugar levels and raised cholesterol level. Metabolic syndrome is not uncommon. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in adult Malaysian was reported as high as 37.1%.
Diagnosis
1. International Diabetes Federation (IDF)
- Increased waist circumference
- > 102 cm (male)
- > 88cm (female)
- > 90 cm (Asian male)
- > 80 cm (Asian female)
Plus 2 or more of the following:
- BP > 130/ 85mmHg or on treatment for hypertension
- Fasting plasma glucose ? 5.6 mmol/L or on treatment for Hyperglycaemia
- Hypertriglyceridemia: Triglycerides ? 1.7 mmol/L
- Decreased high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL)
- < 1.03 mmol/L (male)
- < 1.29 mmol/L (female)
2. National Cholesterol Education Program – Adult Treatment Panel III (NCEP-ATP III)
Any three (3) of the following:
- Abdominal Obesity
- Waist circumference
- > 102cm (male)
- > 88cm (female)
- Waist circumference
- Triglycerides >1.7 mmol/L or on treatment for elevated triglycerides
- HDL cholesterol
- <1 mmol/L (male)
- <1.3 mmol/L (female)
- Blood pressure ?130/85 mmHg or on treatment for elevated BP
- Fasting plasma glucose ?5.6 mmol/L or on treatment for elevated blood glucose
Risk Of Cardiovascular Disease
Metabolic syndrome is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Treatment
1. Lifestyle Modification:
- Diet : Low salt, low glycemic index, and low cholesterol diet
- Exercises : 30 minutes daily
- Quit Smoking
- Weight loss
2. Pharmacology Treatment
3. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Oral hypoglycemic agents
4. Hypertension: Antihypertensive agents
5. Hypercholesterolaemia: Lipid- lowering agents
References
- Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Hypertension 3rd Edition. February 2008.
- Mohamud WN, Ismail AA, Sharifuddin A, Ismail IS, Musa KI, Kadir KA, Kamaruddin NA, Yaacob NA, Mustafa N, Ali O, Harnida S, Bebakar WM. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and its risk factors in adult Malaysians: results of a nationwide survey. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011 Feb;91(2):239-45. Epub 2010 Dec 13.
- Robert H. Eckel. The Metabolic Syndrome. Harrison’s Principle of Internal Medicine 17th Edition. Volume II, 1509-1514
Body/ Support/ Related website
- Malaysian Association for the Study of Obesity
- Malaysian Endocrine and Metabolic Society
- Malaysian Society of Hypertension
- Persatuan Diabetes Malaysia
- www.myhealth.gov.my
| Last Reviewed | : | 2 March 2016 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Lim Chong Hong |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Ainol Shareha Binti Sahar |
 PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia
PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia