In general, drug is defined as a chemical used to prevent, control and treat diseases. Despite of that, it is also classified as toxin group that may cause acute symptoms (poisoning symptoms) if medications instructions are not complied by the patient.
In line with the rapid development of information technology, recently we often hear cases of drug poisoning, especially among children, thus inviting anxiety among consumers to consume medicines. Though medication errors are rare, it should not be neglected by all parties because it can happen anywhere anytime, including at patient’s home.
National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention (NCCMERP) of the United States defines a medication error as:
“Any preventable event that may cause or lead to inappropriate medication use or patient harm while the medication is in the control of the health care professional, patient, or consumer.”
Errors can occur at all stages in the process of taking medicines, either directly or indirectly. It is happen less among adult as the drug information was given directly to them. However, for children, the medication is usually given to caregivers or parents and they will administer it to the children. This process may result in medication errors if it is not given accordingly and medication information was interpreted wrongly by the caregivers.
Therefore, parents or guardians should play an important role in order to equip themselves with adequate information so that medication error can be prevented.
TIPS
9 tips to avoid medication error:
- Know your medicine
Right User

Ensure that the right child is taking the medicine by checking the name on the label of medicine.
Right Medicine

Parents or guardians need to know the generic name of the medicine and the purpose it is given. It is important as the drug’s brand may be changed later. Other than that, the color, shape and markings on the drugs should also need to be identified to avoid confusion.
Right Dose

Parents or guardians should also take into knowledge the quantity and strength of the medicine need to be taken as directed.
Right Time

Parents or guardians should be aware on the time of administration of the medicine on directed interval.
Right Route of Administration

Parents or guardians should also identify the dosage forms of the medicine and to give them accordingly. This is to ensure that the dose given were adequate to achieve therapeutic effect to the child.
Type of Preparations:
a) Liquid preparation

- Newborn to 1 year old child
- Tips on giving medicine:
- Identify the medicines and the correct preparation of the medicine.
- Hold and lift up baby’s head to 45°.
- Swaddle the baby with blanket or towel.
- Blows the baby’s eyes after the medicine were given so that he/she will swallow the medicine.
- Use appropriate tools to give medicine to avoid the baby refuse to swallow the medicine or vomit it out.
- Do not mix medicine with milk or juice.
b) Liquid preparation, chewable tablet or crushed tablet
- 1 year old to preschooler child.
- Tips on giving medicine:
- Mix medicine with foods or desserts
- Serve your child with his/her favorite drink after he/she takes the medicines.
- Do not scold or punish your child if he/she spurt his/her medicine.
- Praise and hug your child after he/she took the medicine.
c) 5 years and above child who usually can swallow medicine.
- School kids
- Tips on giving medicine
- In some circumstances, parents may need to crush and mix tablet medicine with foods or desserts
- Do not let the children to take medicine out of parent’s knowledge

Accurate measurement is important especially for baby and kids. For liquid medicine, it is more accurate to use measuring tools to avoid incorrect measurement of volume of medicine. There are few types of measuring tools that are suitable and appropriate to give medicine to children based on their age and ability to swallow medicine.
| Types | Group of Children | Picture |
| Measuring dropper and oral syringe | Baby and infant/ toddler
– Measure medicine on eye level and give the medicine immediately |

|
| Measuring spoon | Children who cannot drink from cup | 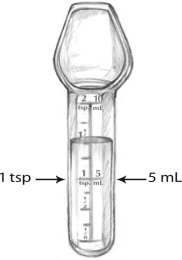 |
| Measuring cup | Children who can drink from cup |  |
 Ask Question
Ask Question
Ask question if you find out that you received a different medicine from previous.
- Keep a list of medicines
 Parents/guardians are encouraged to list out all of medicines their children are taking including vitamins and supplements as well as medicines that cause their children to have allergic reactions. The list should be brought and discussed with doctors or pharmacist whenever they seeing them. It is also should be updated if there is any changes.
Parents/guardians are encouraged to list out all of medicines their children are taking including vitamins and supplements as well as medicines that cause their children to have allergic reactions. The list should be brought and discussed with doctors or pharmacist whenever they seeing them. It is also should be updated if there is any changes.
- Read medicine’s label
 Parents/guardians should read medicine’s label each time before they serve medicine to their children. It is because, the label contains adequate information on how to give the medicine. The label should be read under sufficient lighting to avoid any errors. Check the label to see whether the medicine contains ingredients your child allergic to. Ask for pharmacist’s help if you have any problem in reading the label.
Parents/guardians should read medicine’s label each time before they serve medicine to their children. It is because, the label contains adequate information on how to give the medicine. The label should be read under sufficient lighting to avoid any errors. Check the label to see whether the medicine contains ingredients your child allergic to. Ask for pharmacist’s help if you have any problem in reading the label.
- To inform healthcare providers if have any allergy
 Tell doctors or pharmacists if your kids have any allergies to medicines or foods.
Tell doctors or pharmacists if your kids have any allergies to medicines or foods.
- Price differences: ask them
 If you find out that your child’s medicine’s price is differs hugely from the last time you purchased it, ask the pharmacist in charge. It may be a different medicine with almost similar name.
If you find out that your child’s medicine’s price is differs hugely from the last time you purchased it, ask the pharmacist in charge. It may be a different medicine with almost similar name.
- Do not change the physical of the medicines
 Do not chew, crush or mix medicine with other medicine unless you were told to do so by the doctors or pharmacists. Parents/guardians should ask pharmacists on how and tools to be used to crush or mix medicines.
Do not chew, crush or mix medicine with other medicine unless you were told to do so by the doctors or pharmacists. Parents/guardians should ask pharmacists on how and tools to be used to crush or mix medicines.
- Do not share medicines
 Sharing medicines with others may cause interaction with current medicines. Even the medicine is same, the dose may not suitable to other children and may cause allergic reaction to them.
Sharing medicines with others may cause interaction with current medicines. Even the medicine is same, the dose may not suitable to other children and may cause allergic reaction to them.
- Correct storage of medicine
 Medicines should be stored in original container or envelopes because some medicines have similar appearances and may cause confusion to parents/caregiver when they want to administer it. It may also cause interactions if it was mixed with other medicines or foods. Other than that, the original containers/envelopes may have special criteria that protect the medicines. Furthermore the original containers were labeled completely.
Medicines should be stored in original container or envelopes because some medicines have similar appearances and may cause confusion to parents/caregiver when they want to administer it. It may also cause interactions if it was mixed with other medicines or foods. Other than that, the original containers/envelopes may have special criteria that protect the medicines. Furthermore the original containers were labeled completely.
The medicines should be kept away from heat, high moisture and children. However, it depends on types of medicine. You can refer to pharmacist for specific storage instruction.
- Do not use expired or changed colour medicine
 Parents/guardians are advised to not use medicines that had changed colour or smell, stick to each other, cracked or expired. They should return the medicines to pharmacy for safer disposal.
Parents/guardians are advised to not use medicines that had changed colour or smell, stick to each other, cracked or expired. They should return the medicines to pharmacy for safer disposal.
For further questions, you can contact National Pharmacy Call Centre (NPCC) on 1-800-88-672.
References
- Hadijah bt. Mohd Taib. Cara Pemberian Ubat Kepada Kanak-Kanak; [serial on the Internet]. 2012 April. Available from: http://www.myhealth.gov.my/index.php/ubat-a-anda/umum/cara-pemberian-ubat-kepada-kanak-kanak
- Raudhatun Sa’adiah Ithnin. Waspada Elak Keracunan Ubat.Dlm. Harian Metro 2015; April12: E7
| Last Reviewed | : | 6 October 2017 |
| Writer | : | Raudhatun Sa’adiah Ithnin |
| Translator | : | Raudhatun Sa’adiah Ithnin |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Zarina Banu Binti Abdulla |
 PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia
PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia