OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNEA AND UNCONTROLLED BRONCHIAL ASTHMA- WHAT IS THE LINK?
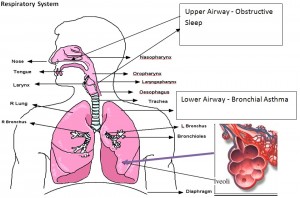
Obstructive Sleep Apnea Hypopnea Syndrome (OSAHS) and asthma are 2 diseases of the common airway.
Asthma affects the lower respiratory tract or also known as the lower airway.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea Hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS) affects the upper respiratory tract or also known as the upper airway.
Source : www.ambulancetechnicianstudy.co.uk
Obstructive Sleep Apnea – Hypopnea Syndrome (OSAHS)
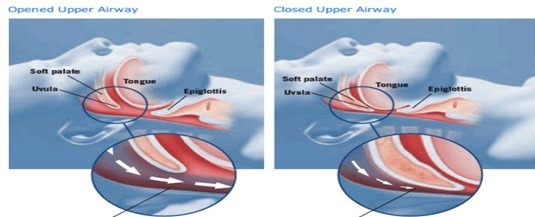
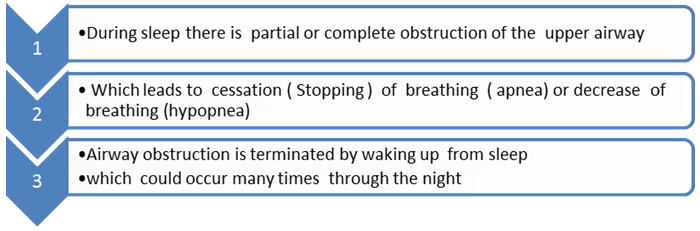
It is a cessation (stopping) or pauses in breathing that occur when an individual is asleep. This occurs due to upper airway collapse (blockage to air flow in the upper airway) during sleep.
It commonly occurs in obese people.
What happens when you sleep if you are at risks of developing OSA
Risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea (OSAHS)
- Obesity
- Males
- Large neck size (circumference >40 cm)
- Abnormal fascial structures nasal, throat soft tissue abnormalities
- Smoking
- Advancing age
- Family history
The most common obstructive sleep apnea symptoms include:
- Daytime sleepiness or tiredness
- Snoring
- Dry mouth upon awakening
- Headaches in the morning
- Trouble concentrating, forgetfulness, depression, or irritability
- Restlessness during sleep
Asthma
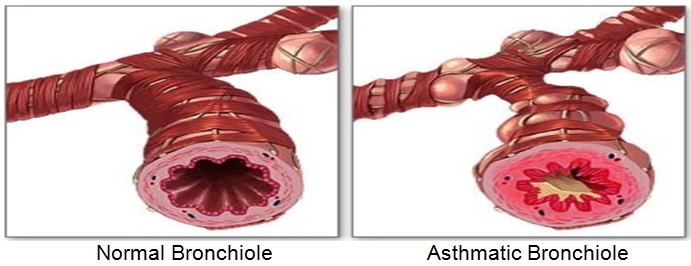
Asthma is due to inflammation of the lower respiratory tract. Asthma presents as intermittent airway constriction due to bronchial hyper responsiveness (hyperactivity).
During an asthma attack, smooth muscles located in the bronchioles of the lung (the lower airway) become narrowed which causes decrease of air flow in the airways.
Common symptoms of asthma
- Coughing, especially at night
- Wheezing
- Shortness of breath
- Chest tightness
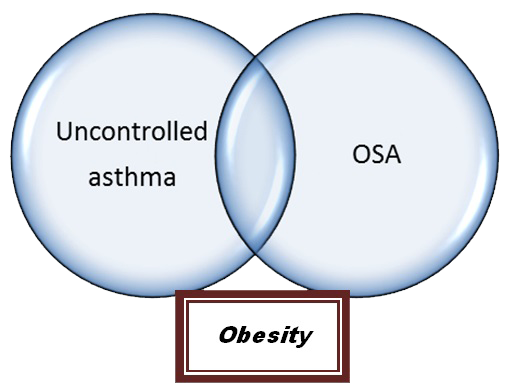
Asthma and OSA have common risk factors and one of them is obesity.
Night symptoms of cough, wheezing, shortness of breath, gasping for breath may represent asthma or other conditions like OSA.
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome has been shown to be associated with inflammation of both the upper and lower respiratory tracts.
Unrecognized obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) may lead to poor asthma control during sleep due to oxidative stress and inflammation despite optimal therapy for the treatment of asthma.
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is an important contributor to poor asthma control. Treating OSA may lead to better control of asthma. If you have uncontrolled asthma and symptoms of OSA, discuss with your doctor .
How Is Obstructive Sleep Apnea Diagnosed?
To diagnose obstructive sleep apnea, your doctor will
- Take a medical history
- Sleep history – from you and people who live with you about your sleep habits – eg snoring , restless sleep, repeated awakenings during sleep, gasping or choking during sleep
- Clinical examination will be done to ascertain OSA
If you have symptoms and you are at risk of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
You will be required to take a sleep study called Polysomnography or PSG. It is an overnight study that can be performed in the hospital sleep lab or a portable sleep study that can also be done at home.
What you will need to do is to sleep overnight.
The test will measure:
- Your sleep
- Air flow and oxygen levels while you are asleep
- Your breathing pattern
- Electrical activity of the brain
- Heart rate
- Muscle activity
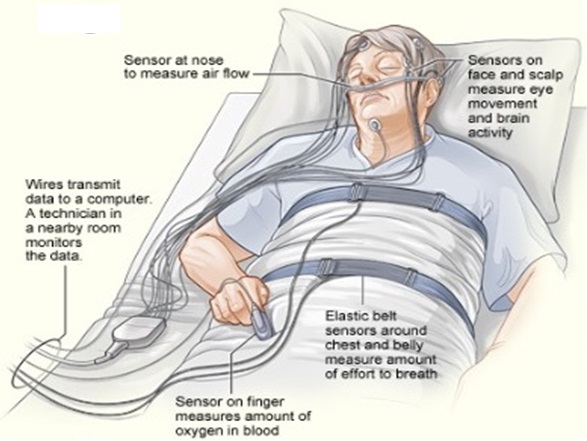
This is how a sleep study is performed
A polysomnogram – is the final result of the sleep study. Your doctor will inform you how severe your OSA is based on the sleep study.
Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Asthma
You should continue using your asthma medication as advised by your doctor.
Changes in lifestyle- weight loss in overweight patients – may be sufficient to control sleep apnea in mild cases and should also be in the treatment plan in severe cases.
Stop smoking – smoking is known to cause worsening of asthma and OSA.
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) – CPAP therapy is the only treatment that is 100% effective in treating Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA).
The CPAP machine provides a positive pressure that will hold your airway open while you are asleep. This prevents snoring and the airway collapse causing OSA.
The CPAP machine connects to a mask that you can wear over your nose and/or mouth during sleep.
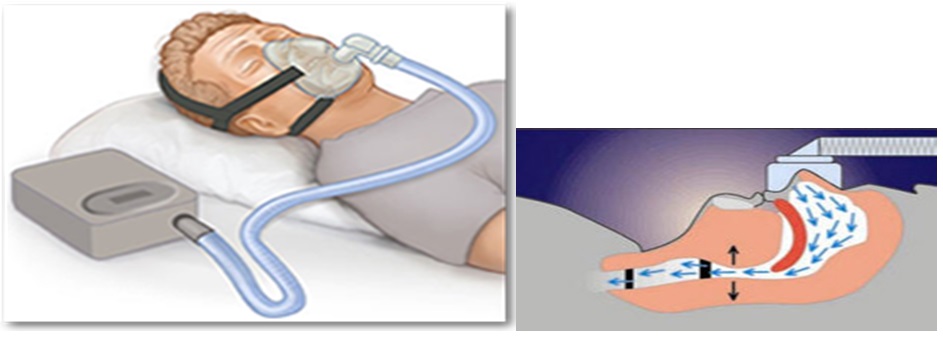
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) treatment of OSA in patients with asthma improves asthma symptoms and asthma-specific quality of life.
References:
- Sleep apnea: A proinflammatory disorder that coaggregates with obesity. Reena Mehra, MD, MS and Susan Redline, MD, MPH. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
- Nocturnal asthma: role of snoring and obstructive sleep apnea.Chan CS, Woolcock AJ, Sullivan CE. Am Rev of Respr Dis 1988 Jun;137(6):1502-4.
- Nocturnal asthma: snoring, small pharynx and nasal CPAP. Guilleminault C, Quera-Salva MA, Powell N, Riley R, Romaker A, Partinen M, Baldwin R, Nino-Murcia G. Eur Respir J. 1988 Dec; 1(10):902-7.
- Association of obstructive sleep apnea risk with asthma control in adults. Teodorescu M, Polomis DA, Hall SV, Teodorescu MC, Gangnon RE, Peterson AG, Xie A, Sorkness CA, Jarjour NN. Chest. 2010 Sep; 138(3):543-50. Epub 2010 May 21.
- Impact of CPAP on asthmatic patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Lafond C, Sériès F, Lemière C. Eu Respr Journal Feb;29(2):307-11. Epub 2006 Oct 18.
- Risk factors of frequent exacerbations in difficult-to-treat asthma. Eu Respr Jpurnal 2005 Nov;26(5):812-8. Ten Brinke A, Sterk PJ, Masclee AA, Spinhoven P, Schmidt JT, Zwinderman AH, Rabe KF, Bel EH.
- Characteristics and mechanisms of nocturnal asthma. Martin RJ. Allergy Proc 1993 Jan-Feb;14(1):1-4.
| Last Reviewed | : | 17 March 2016 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Jasminder Kaur |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Jamalul Azizi b. Abdul Rahaman |
 PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia
PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia