Kidney
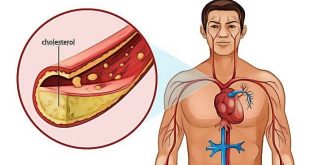
High blood pressure (hypertension) is the second most common cause of chronic kidney disease in Malaysia. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a long-term condition where the kidneys do not work well as normal.
As a result, the kidneys are less able to do the following jobs to help maintain health:
- Remove wastes and extra fluid from the body
- Release hormones that help to:
- Control blood pressure
- Promote strong bones
- Prevent anemia by increasing the number of red blood cells in the body
- Keep the right balance of important chemicals in the blood, such as sodium, potassium, phosphorus and calcium
- Maintain the body’s balance of acid and base
CKD may eventually lead to kidney failure. End-stage kidney failure requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant to maintain life. Early detection and treatment can prevent or delay the complications.
How Does High Blood Pressure Cause Damage To The Kidneys?
High blood pressure can damage blood vessels throughout the body. This can reduce the blood supply to important organs like the kidneys. High blood pressure also damages the tiny filtering units in the kidneys. As a result, the kidneys may stop removing wastes and extra fluid from the blood. The extra fluid in the blood vessels may build up and raise blood pressure even more.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)?
The symptom of kidney disease is variable according to the stage of the disease. In early stage of kidney disease, it usually does not have any symptoms. Thus, people may have CKD but not knowing it because they do not feel sick. At the late stage of CKD, the following symptoms might happen :
- Progressively reduce effort-tolerance
- Fluid retention, especially in the lower legs during evening/prolonged standing
- Recurrent nausea/ vomiting
- High/worsening blood pressure
- Decrease in amount of urine
Protein in the urine (Proteinuria) is an important sign of CKD. These patients pass out frothy urine. It can be confirmed through urine test. Healthy kidneys remove waste produce out of the blood but retain protein. Diseased kidneys may fail to separate a blood protein called albumin from the wastes.
At the beginning, only small amounts of albumin leak into the urine, a condition known as microalbuminuria. This is an early sign of kidney disease. As kidney disease progress, the amount of albumin in the urine increases, and the condition is called proteinuria.
 Figure 1: Frothy Urine With Confirmed Proteinuria
Figure 1: Frothy Urine With Confirmed Proteinuria
How To Confirm CKD In Hypertension?
The following tests need to be done by the treating physician to confirm CKD :
- Blood test to measure renal function
Cretinine is a waste product from normal breakdown of muscle cells. Healthy kidneys take creatinine out of the blood and put it into the urine to leave the body. When the kidneys are not working well, creatinine builds up in the blood. Creatinine is used to measure the glomerular filtration rate, or GFR. GFR is a measurement of how well the kidneys are filtering wastes from the blood. If the GFR is too low, it may indicate the kidneys are not able to remove enough wastes and extra fluid from the blood.
 Figure 2: Blood Taking For Investigation
Figure 2: Blood Taking For Investigation
- Urine test for protein and red blood cells
Persistent protein or/and red blood cells in the urine is a sign of kidney damage. An increased urine protein means that is a higher chance the kidney disease will progress.
How To Prevent Kidney Damage From High Blood Pressure?
Optimal blood pressure control is essential to prevent kidney damage from high blood pressure. Medication and lifestyle changes can help to lower blood pressure.
Healthy lifestyle choices include not smoking, eating a healthy diet, staying fit, maintaining an appropriate weight, avoiding certain medications and avoiding stress.
In the management of hypertension in kidney disease, control of BP and proteinuria are the most important factors in retarding the progression of kidney disease. Anti-hypertensive medications that reduce proteinuria thus have an advantage. For example, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are commonly used as first-line of anti-hypertensive medications.
In hypertensive patients with proteinuria, the target blood pressure should be as stated below.
- <130/80 mmHg for those with proteinuria of >1g/24 hours
References
- Clinical practice guidelines for management of chronic kidney disease in adults, Malaysia
- Figure 1: http://www.transplantbuddies.org/tbx/messages/7/419778.html?1299424414
- Figure2:http://www.mudframes.com/2011/07/18/world-hepatitis-day-2011-malaysia-campaign-in sunway-pyramid/_mg_0618/
- Figure 3: http://seh.50megs.com/central_activity.htm
| Last Reviewed | : | 31 December 2013 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Yeoh Chin Aun |
| Translator | : | Dr. Yeoh Chin Aun |
| Akreditor | : | Dr. Anita Bhajan |
 PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia
PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia