Diabetic Foot
It is important for diabetic patients to take care of their feet.
There are many types of foot problems commonly occurring among diabetics such as :
- Athlete’s foot (a fungal infection)
- Calluses and corns (hardened areas of skin),
- Cuts and blisters,
- Bunions (enlargement of bone tissue around the joint at the head of the big toe)
- Foot deformities.
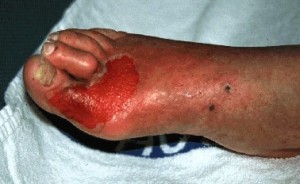
Poor diabetic control and foot care will progress to foot ulcers that can range from a surface wound to a deep infection. Below are some illustrations of diabetic foot.
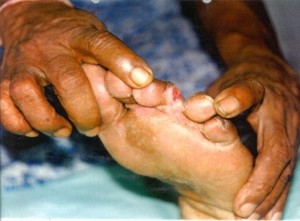 |
 |
| Athlete’s foot | Blisters & Calluses |
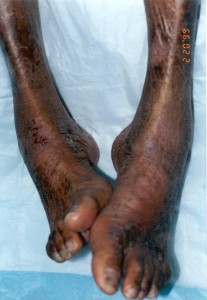 |
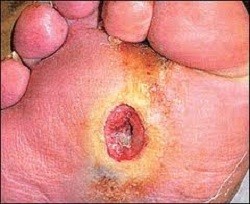 |
| Foot deformities | Foot ulcer |
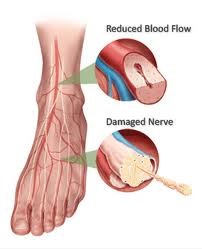
What Causes Diabetic Foot :
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
- Elevated blood glucose levels over time can damage the nerves of the foot, decreasing a person’s ability to feel pain and pressure.
- These predispose to development of callused pressure spots and will eventually injure the skin, soft tissue, bones, and joints.
- Over time, the bone and joint damage can alter the shape of the foot.
- Nerve damage, called neuropathy, can also weaken certain foot muscles, which further contributes to foot deformities.
- Footwear
- Poorly fitting shoes is a common cause of diabetic foot.
- They will start with red spots, sore spots, blisters, corns, or calluses.
- Those with foot abnormalities such as flat feet, bunions or hammertoes are also at risk of diabetic foot if the footwear is inappropriate.
- Trauma to the foot
- Any trauma to the foot can increase the risk for a more serious problem to develop.
- Infections
- Athlete’s foot, a fungal infection of the skin or toenails, can lead to secondary bacterial infections and should be treated promptly.
- Ingrown toenails should be handled right away with caution. It occurs when the corner or side of the toenail grows into the soft flesh. Get help from your doctor.
- Smoking
- Smoking causes damage to the small blood vessels in the feet and legs.
- This damage can disrupt the healing process and is a major risk factor for infections and amputations.
What You Should Do If You Have Diabetic Foot ?
- Optimize your diabetes control
- Controlling blood sugar levels can reduce further damage to blood vessels and nerves, which helps in wound healing and reduces the risk of amputation.
- Stop smoking
- This is the best thing you can do to prevent foot complications.
- Adhere to foot care recommendations for diabetics
- Ask your doctor or health provider and refer to Diabetic Foot Care recommendation/pamphlet. Refer to notes on foot care.
- Seek treatment early and follow your doctor’s advice
- Treatment depends upon the types and severity of the foot problems.
- Superficial ulcers (involving only the top layers of skin) – includes cleaning the ulcer and removing dead skin and tissue by a healthcare provider.
Foot from a diabetic patient showing a superficial ulcer (Wagner grade 1) that involves the full thickness of the skin but no underlying tissues. This lesion healed quickly with rest and local foot care.
- If the foot is infected, antibiotics are prescribed. Ulcers should be cleaned and dressing applied twice daily.
- You should keep weight off the foot ulcer as much as possible, meaning that you should not walk with the affected foot. The foot should be elevated when sitting or lying down. The ulcer should be checked by a healthcare provider regularly to make sure that the ulcer is improving.
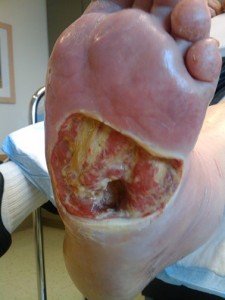
- Ulcers that extend into the deeper layers of the foot, involving muscle and bone, usually require hospitalization.
- More extensive laboratory testing and x-rays may be required, and intravenous antibiotics are often necessary. Surgery may be necessary to remove infected bone. A plaster cast on the foot may be required to take pressure off the ulcer.
The patient presented with a fluctuant abscess on the plantar surface of the foot. The abscess was unroofed and drained, and, following debridement, exposed bone was apparent at the base of the wound.
- If part of the toes or foot become severely damaged causing gangrene (tissue death due to inadequate blood supply), amputation may be required.
- Amputation is reserved for patients who do not heal despite aggressive treatment, or whose health is threatened by the gangrene. Untreated gangrene can be life-threatening.
- Those with severe foot ulcers and peripheral vascular disease (poor circulation) may require a procedure to restore blood flow to the foot.
- Home health care : The patient may need an aide to help with wound care and dressings, monitor blood sugar, and taking medication properly during the healing period.
Conclusion
Recognition of risk factors, preventive foot maintenance and regular foot examinations are essential in preventing foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. When foot ulcers develop despite all preventive measures, early and appropriate treatment, should help to reduce the tremendous personal and societal burden of diabetes-related amputations.
References
- Ministry of Health Malaysia : Malaysian CPG : Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Kuala Lumpur : Academy of Medicine Malaysia;
- Armstrong D.G, Lavery L.A. Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Prevention, Diagnosis and Classification, Am Fam Physician1998 ;15;57(6):1325-1332.
- Diabetic Foot Care : http://www.emedicinehealth.com/script/main/art (accessed on 11th May 2013).
Quiz
- What are the main causes of diabetic foot?
- damaged nerves
- narrowing of blood vessels
- decreased skin sensation
- All these are due to longstanding high glucose levels in the blood.
- Why do diabetic patients tend to ignore their foot ulcer until it becomes big?
A : People with diabetic foot has neuropathy (nerve damage) causing loss of sensation. Thus they will not feel the pain and are not troubled by their ulcer during the early stage.
 PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia
PENDIDIKAN PESAKIT Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia